Monday June 15th 2020 by SocraticDev
Fuzzy logic is based on the theory of fuzzy sets developed by the mathematician and engineer Lotfi Aliasker Zadeh in 1965. Fuzzy logic facilitates the modeling of logical reasoning operated on vague or imprecise propositions like "Elena is young" or "The water is hot". It belongs to the family of many-valued logics. Contrary to classical logic operating on two truth values (true and false), fuzzy logic allows inferences to be drawn from premises which are neither true nor false, but which have a certain degree of truth.
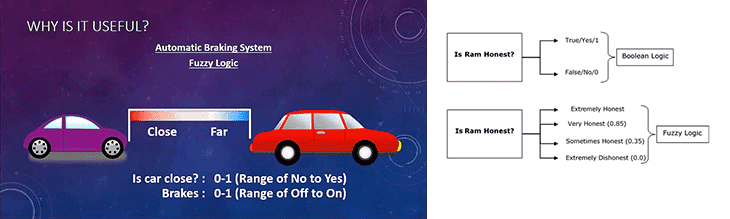
Being more nuanced and flexible, fuzzy logic is akin to human reasoning. To the question "Is it sunny outside today?", Classical logic forces us to answer "Yes" or "No". When in reality, we will answer that it is perfectly fine (1), more or less fine (0.6) or rather bad weather (0.3).
Why use fuzzy logic?
Fuzzy logic has industrial, commercial and domestic applications. It is useful in the context where it is acceptable for a system to make a decision based on acceptable reasoning, but not 100% certain. In engineering, due to the complexity of the systems and the variability of the inputs, it is often more economical to fall back on fuzzy logic.
Traditional Controllers
- Need to have detailed physical properties of the system
- Most systems are too complex and must be idealized in order to develop a traditional controller
- i.e. We do not have access to a representation of the entire system
- The traditional controller can only operate in a context where conditions are limited
Fuzzy Controllers
- No need to have a deep knowledge of the system
- the decisions to be made by the controller are determined by linguistic rules
- By using optimization tools such as genetic algorithms, we can get by without knowing anything about the system
- The system does not need to be reduced or idealized to develop the controller
- The controller is more robust because it tolerates great variability in the inputs
Caracterizing a fuzzy function
A fuzzy function takes a Crisp Input and returns a Crisp Output. First, the input is fuzzified by a 'fuzzifier' function. That is, it is translated into fuzzy sets.
The Membership function is a graph defining how each point of the entry is linked to a value between 0 and 1 according to linguistic terms. The membership function represents the degree of membership of a fuzzy set to a universe of discourse.
For example, you could use fuzzy logic to determine whether "the water temperature in the hotel pool is comfortable". In addition to the net entry (current pool water temperature), the function will also quantify the linguistic terms such as "pleasant" or "unpleasant" in order to answer the question with a net exit: Yes or No.
Fuzzy logic is not probabilities
Fuzzy logic is not linked to the notion of probability
- Fuzzy logic is linked to the concept of truth while probability is linked to the concept of knowledge.
- Fuzzy logic is mainly interested in the essence of the notion of imprecision while probability is interested in events: whether these events will take place or not.
- Fuzzy logic has a mathematical basis and divides truth into degrees of truth. As for probability, it is the mathematical modeling of ignorance about future events.
Translated from french by Google Translate
Sources
https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/logic-fuzzy/
An Introduction to Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy Logic in Artificial Intelligence | Introduction to Fuzzy Logic & Membership Function | Edureka
